Long Range UT (LRUT) / Guided Wave
Long Range Ultrasonic Testing (LRUT) is an efficient technique used to test large volumes of material from a single test point.
Details
LRUT for the in-service surveying of metal loss in pipelines and piping was developed in the 1990’s through a UK Technology collaboration of Imperial College and the Research Institute TWI which culminated in the release of the first Guided Wave testing product Teletest® in 1998, today known as Eddyfi Technologies’ Sonyks™. This technology was further improved over the next 20 years until the brand was sold to Eddyfi Technologies in September 2017.
The impetus for the development of LRUT is that ultrasonic thickness checks for corrosion, erosion, etc. are very localized, in that they only measure the thickness of the area under the UT transducer.
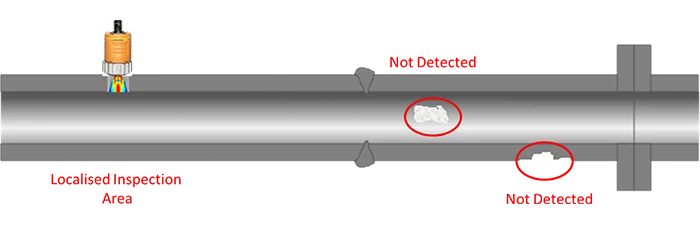 Localized, single-point inspection
Localized, single-point inspection
The operation of the LRUT technique is shown schematically in the figure and Sonyks uses low frequency guided ultrasound travelling along the pipe providing 100% coverage of the pipe wall without moving the transducer tool.
Depending on pipe conditions, up to 350 metres of pipework can be inspected from a single test point. LRUT reduces the costs of gaining access and avoiding extensive removal of insulation (where present). The whole pipe wall is tested, achieving a 100% examination (including areas such as at clamps, and sleeved or buried pipes).
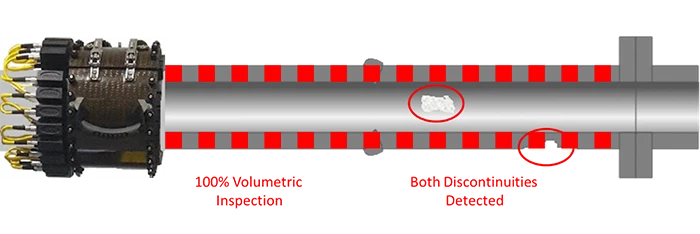 Long Range UT inspection
Long Range UT inspection
Continuous development
The development and improvement of LRUT has been rapid over the first 20 years since the first product has been commercially available. The equipment can now generate and fully utilise any of the three main Guided Wave types (longitudinal, torsional and flexural). There has also been significant developments in utilising phased-array technology making it possible to focus the ultrasound and analyse the circumferential responses of potential defects. In addition, the boundaries for inspection has increased such that the inflatable collars, modules and transducers are capable of inspecting pipe sizes up to 78” and increased temperature capability of 240°C.
Ask an Expert
Inspection sensitivity
The earliest work showed that the smallest area of metal loss which LRUT can detect is approximately 3% of the pipe wall cross-section. The reporting level which is normally used is a signal amplitude equivalent to 9% area, to ensure that false call rates are kept to an acceptable level. These thresholds were verified through 'blind trials' without knowledge of any defects and the results were independently evaluated. In all of the independent trials conducted over the last 20 years LRUT operators have found all defects over 4.5% cross-sectional area loss over a variety of pipe sizes and pipe conditions.
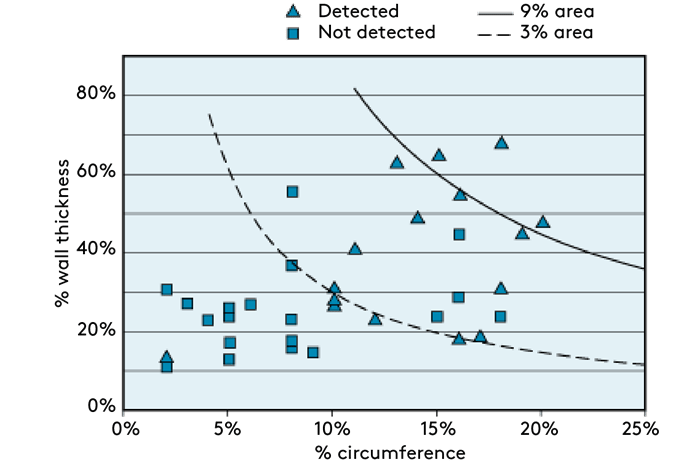
The main factors which affect the sensitivity of LRUT are:
- The size of the corroded area, as 'seen' by the wave propagating along the pipe. Detectability is related to the proportion of the pipe wall cross-section which is lost (the combination of the depth and the circumferential extent).
- The axial extent of the corroded area. The technique is less sensitive to this dimension, although long defects produce a stronger signal than shorter ones.
- Pipe features. All discontinuities affect the ultrasound signals and therefore give rise to responses, such as butt welds, bends, attachments, etc.
- Coatings. Some types of coating affect the rate of attenuation of the ultrasound and therefore reduce the test range achievable.
- Test sensitivity. To perform an adequate test, a certain level of ultrasound has to be generated (a minimum signal-to-noise ratio), in order to maintain the expected sensitivity to defects.
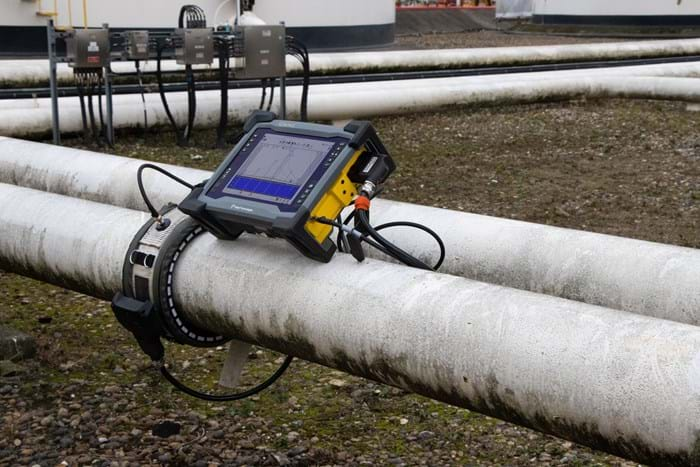

Well suited for many applications
Long-range ultrasonic testing using guided waves is one of the few test methods which is able to examine 100% volume of pipe wall from one tool location so has found widespread applications in non-piggable pipeline where efficient inspection coverage is required or the pipeline in question has hard to reach areas. Successful inspections have been carried out in the following applications:
Learn more
Tank farm pipework
- Long lengths of pipes
- Insulated line
- Link lines
- Jetty line inspection
- Bund wall penetrations
- Culvert Inspection
- Road crossings
Refinery pipework
- Corrosion under Insulation
- Corrosion at simple
- Pipe-supports
- Hot pipe inspection – max 350°C
- Inspection of elevated pipe
- Flare line inspection
- Jetty pipe work
Offshore Applications
- Corrosion under insulation
- Riser inspection
- Deck penetrations
- Splash zone inspection
- Fretting on Caissons
- Caisson inspection
- Topside pipework
- Seals for deck hatches and fire seals
Other inspections
- Road Crossings
- River Crossings
- Transmission lines
- Unpiggable pipelines
- Buried pipelines
- Insulated Sphere legs
- Air-soil interface








